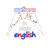Call Options for Beginners
If you want to learn about Call Options you have come to the right place. In this introductory lesson you will learn what Call Options are and what they can do for you. You don't need to have any prior knowledge or experience with them. We will lay down the foundation upon which you can build your option trading expertise.

Put Options for Beginners
Put Options are versatile and widely used financial instruments that allow investors to profit from price declines as an alternative to outright short selling. They have also found a place in many investors' portfolios as protection or hedge against price declines. You will learn what Put Options are and how you can use them whether you have some experience with them or none at all.
Risk Profile: Buying a Call
In this lesson we will analyze the risk profile of a Long Call Strategy, its pros and cons and also how this translates into an actual trade. We will also use our trading platform to go through the process of buying a call, as well as a detailed analysis of what-if scenarios based on its risk profile.
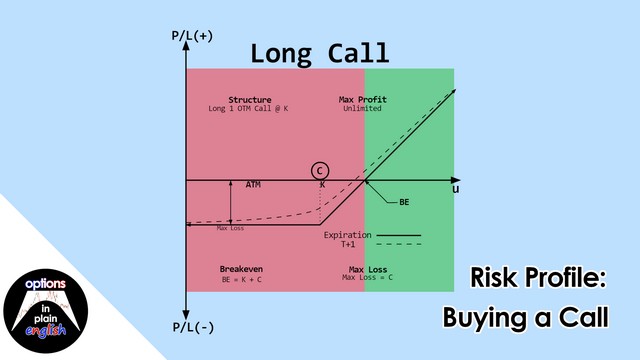
Risk Profile: Buying a Put
In this lesson we will analyze the risk profile of a Long Put Strategy, a bearish strategy designed to profit from down moves in the market. We will also use our trading platform to go through the process of buying a put, as well as a detailed analysis of what-if scenarios based on its risk profile. Additionally we will briefly look at using a put as protection for long holdings.

At the Money, In the Money, Out of the Money
Traders refer to Options' Strike Prices that are At the Money, In the Money and Out of the Money. Learn what this means and how to determine which Calls and Puts are ATM, ITM and OTM.

Intrinsic and Extrinsic Values
An Option's Price is made up of two components: Intrinsic and Extrinsic Values. Learn what they mean and their similarities and differences as we analyze real examples of Calls and Puts in the Options Market.

Factors Determining an Option's Price
In this lesson you will learn the factors that determine an Option's price. We will analyze Underlying Price, Strike Price, Time to Expiration, Volatility, Dividends and Interes Rates.

Introduction to Volatility
Volatility is a very important concept in Options Trading. In this introductory lesson you will learn what Volatility is conceptually and how it affects Option Prices in practice.

Historical and Implied Volatility
In this lesson you will learn the differences and similarities between Historical and Implied Volatility. You will also see why Option Traders pay so much attention to an underlying's Implied Volatility while using its Historical counterpart as reference at best.

Expected Price Range based on Implied Volatility
Implied Volatility can be used to determine the statistical range of potential future prices for an underlying. We will derive and apply both the normal distribution approximation and also the version for a lognormal distribution of stock prices based on current Implied Volatility. We will see that in most cases, the normal approximation is sufficient for us to use in options trading.

Option Greeks: Delta
We start our analysis of Options Greeks with perhaps the most important of them all: Delta. You will learn how Delta represents the change in Option Price for every $1.00 of Underlying Price change. In addition to this, we will discuss Delta's use as proxy for Probability of expiring in the money and also how it can help us determine adequate hedging ratios for existing positions.
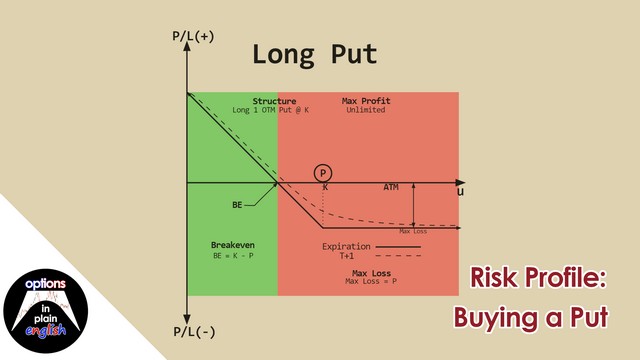
Risk Profile: Selling a Put
In this lesson we will analyze the risk profile of a Short Put Strategy; its advantages and disadvantages, margin considerations and how to structure it. We will also discuss the use of short puts as a strategy for purchasing stock at a discount. Finally, we will use our trading platform to go through the process of selling a put, both in a cash and also in a margin account, as well as a detailed analysis of what-if scenarios based on its risk profile.
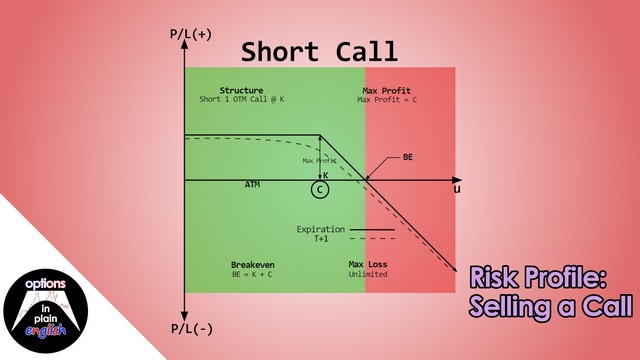
Risk Profile: Selling a Call
In this lesson we will analyze the risk profile of a Short Call Strategy; its advantages and disadvantages, margin considerations and how to structure it. We will also discuss the use of short calls as part of a strategy for selling premium and enhancing yield on existing holdings called Covered Call. Finally, we will use our trading platform to go through the process of selling a call, and also initiating a Covered Call, as well as a detailed analysis of what-if scenarios based on its risk profile.

Types of Volatility
If you have ever been confused and overwhelmed by the different types of Volatility that you have seen or heard about this is the lesson for you.

Liquidity in Options Trading
Liquidity is one of the most important and unfortunately often overlooked aspects of Options Trading. In this lesson we will take a look at what Liquidity means when you trade options and what you need to focus on when you are determining whether an underlying's options are liquid enough for you to trade. By the end of this lesson you will know why it is so important that you only trade liquid options regardless of strategy. We will focus on Bid/Ask Spread, Strike Availability, Expiration Availability, Open Interest, Volume and Underlying Volume. All these factors will come into play as you determine whether or not to trade an underlying's options based on its liquidity.

How to calculate Probability of Profit for Option Trades
In this lesson you will learn how to determine a trade's Probability of Profit. We'll review important concepts such as Breakeven price as well as Probability of expiring ITM and Probability of expiring OTM. You will also understand the subtle but important difference between using Delta and Probability of expiring ITM and how it affects the calculations for Probability of Profit. Finally, by applying interpolation you will be able to determine Probability of Profit for any Option trade, as long as your Breakevens are clearly defined.
How to practice Option Trading for Free with paperMoney® by Thinkorswim
Get access to a real trading platform with real market data so that you can get familiar with different Option Strategies before trading with your own capital.
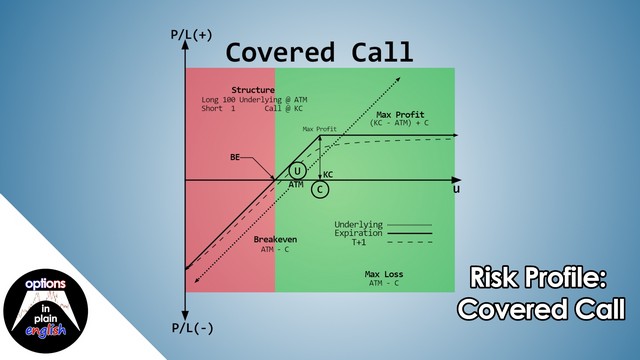
Risk Profile: Covered Call
In this lesson we will analyze the risk profile of a Covered Call strategy; its advantages and disadvantages, margin considerations and how to structure it. We will also discuss synthetically equivalent positions by comparing and contrasting a Covered Call with a Short Put strategy. This will be the first of a series of lessons on strategies where we combine two or more of the 6 basic positions (Long Stock, Short Stock, Long Call, Short Call, Long Put, Short Put) to create customized strategies that take advantage of the flexibility of Options as a trading instrument.

How to read Risk Profile Graphs
In this lesson you will learn how to read and interpret all the information contained in a typical Risk Profile graph. We will focus on the format we use for the strategies we review on our website.

Differences between trading Options and Stocks
In this lesson we will go through the main differences between Options and Stocks as well as differences in the mechanics of the trading process for both. If you are coming over from the Stock trading world into the world of Options trading this will be a quick and easy way for you to get acquainted with the similarities and differences between these two products and how they are traded.
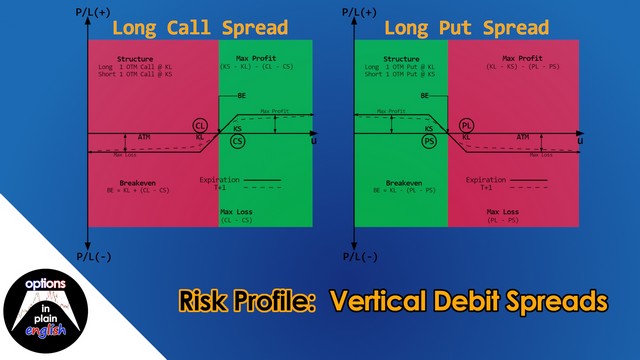
Risk Profile: Vertical Debit Spreads
In this lesson we will analyze the risk profile of Vertical Debit Spreads; their advantages and disadvantages, buying power reduction considerations and how to structure and manage them. Vertical Spreads are one of the most widely used option strategies because of their clear and unambiguous potential max profit and max loss. In addition to this, they can be used to establish positions in expensive underlyings using limited capital where it would not be possible to do so by trading the underlying or standalone options.
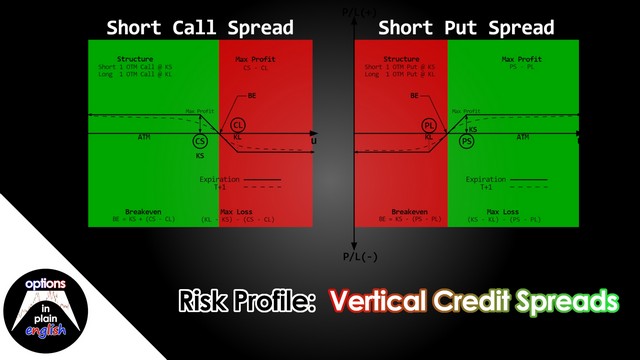
Risk Profile: Vertical Credit Spreads
In this lesson we will analyze the risk profile of Vertical Credit Spreads; their advantages and disadvantages, buying power reduction considerations and how to structure and manage them. Vertical Spreads are one of the most widely used option strategies because of their clear and unambiguous potential max profit and max loss. In addition to this, they can be used to establish positions in expensive underlyings using limited capital where it would not be possible to do so by trading the underlying or standalone options.

Volatility Skew
In this lesson we will talk about Volatility Skew; what it is, how we can see it in action and how we need to account for it as Options Traders. In theory, an underlying should have only one Volatility, representing the standard deviation of its returns over a certain period of time. When dealing with Implied Volatility however, every option, call or put has a price and this price implies a level of Volatility for that particular Option. In this lesson we will analyze how this affects the design, execution and management of options positions considering the existence and nature of its Volatility Skew. We will also look at the different Skew Patterns that traders have identified over the years (Reverse Skew, Forward Skew, Smile, etc.) and where these patterns are most likely to conform to reality.
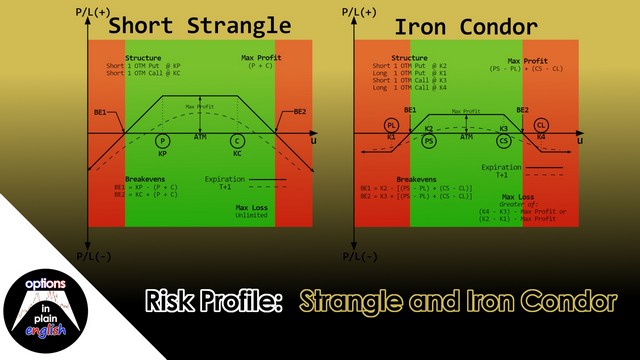
Risk Profile: Strangle and Iron Condor
In this lesson we will analyze the risk profile of Strangles and Iron Condors; their advantages and disadvantages, buying power reduction considerations and how to structure and manage them. We will also determine the market conditions that make these strategies a good fit for your overall portfolio. Strangles are undefined risk positions that take advantage of time decay and Implied Volatility's mean reversion without necessarily having a directional component to them. Iron Condors are similar but define the risk and max loss by working with short spreads instead of short naked options. These are strategies that beginner traders often use when they start looking at delta-neutral positions and how to take advantage of option properties that are not related to a directional outlook.
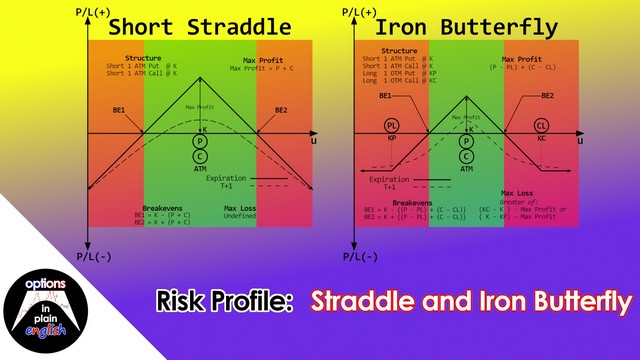
Risk Profile: Straddle and Iron Butterfly
In this lesson we will analyze the risk profile of Straddles and Iron Butterflies; their advantages and disadvantages, buying power reduction considerations and how to structure and manage them. We will also determine the market conditions that make these strategies a good fit for your overall portfolio. A straddle is a very simple strategy, combining a short put with a short call, often At-the-Money. This strategy benefits when the underlying trades inside a range and also when the Underlying's Implied Volatility decreases after the straddle has been initiated.

Option Greeks: Theta
In this lesson we are going to continue analyzing Option Greeks and having already discussed Delta, we'll move on to perhaps the second most important one: Theta Theta measures time decay and is the theoretical amount that an Option would lose after one day assuming everything else stays the same. Options are expiring assets and at expiration their extrinsic value will go to zero. Theta measures this gradual loss of value as time passes. By the end of this lesson you will understand how theta affects your options positions and also how to take advantage of it or at least minimize its effects in your search for more efficient and profitable option trading strategies.

Option Greeks: Gamma
In this lesson we are going to talk about the most important second order Greek: Gamma. Gamma measures how much Delta changes as the Underlying price changes. It is a measure of acceleration of Profits if you are long gamma and an acceleration of losses if you are short gamma. Gamma is what allows your long options to profit more and more as the stock price goes your way, making your deltas go in the direction of the move. This advantage has a cost though. To enjoy the potential acceleration of profits provided by Gamma you will have to lose money due to theta if price doesn't move your way or if it moves against you. We are going to explore this relationship between gamma and theta in this lesson. We will also isolate the effect of gamma in day-to-day P/L by looking at the Delta-Gamma approximation and focusing on the effect of gamma. This will give you a good perspective as to how gamma is reflected in day-to-day profits and overall profits and losses in general.

Option Greeks: Vega
In this lesson we're going to analyze how Volatility affects option pricing by looking at Vega, which measures how an option price changes as Volatility increases by 1 percentage point. A higher Implied Volatility will make options, both calls and puts, more valuable. This is because a higher implied volatility makes larger price swings more probable, and this is reflected in Options' higher premiums. Volatility risk is a real risk that is unfortunately overlooked or misunderstood by many traders. When a trader is short options, an increase in Implied Volatility will make those short options much more valuable, generating losses that can rapidly grow as IV keeps expanding. It is therefore very important that you understand how Implied Volatility can work in your favor when you are long options and how it can work against you when you are short options. Once you have identified this risk, you can incorporate it into your trading plan so you know how to manage it during the life of the trade.
Options 101 for Stock Traders new to options in 9 minutes
If you’ve been trading stocks for a while, and want to start trading options but don’t know where to start, in this video you will learn options basics and see options in action so you can start trading right away
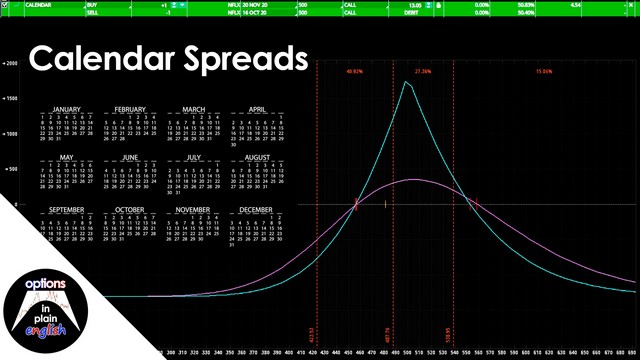
Calendar Spreads
A calendar spread is a strategy made up of two options, either two calls or two puts where one is sold in a certain expiration and the other one is bought in a later expiration but with both calls or puts at the same strike price. These strategies are conservative, slow-moving vehicles that try to capitalize on the accelerated theta in the front expiration and the larger Vega in the back expiration to create a strategy that is both positive Theta and positive Vega while aiming for the underlying to stay inside a price range. In this lesson we will look at Calendar Spreads and how we can make use of them efficiently and incorporate them into our portfolio.

How to trade the VIX
VIX, also called the "Fear Index", represents the 30-day expected volatility of the US Markets as reflected in the price of SPX Options. It is also an index that can be traded, although not as easily as other indices such as the SPX or the NDX. In this lesson we will learn how to trade VIX by using VIX Futures, VIX ETFs and ETNs and also VIX Options. We will also learn the nuances of each one of these instruments, how contango and backwardation affect their pricing and how to select the best instrument to trade the VIX effectively and profitably.

Trading VIX Products
In this lesson we'll analyze SPX, VIX, VVIX and SPX Probability Cones as a way to understand how different Volatility measures are related to the market's price action and also what we can infer from an analysis of the volatility of VIX and what it tells us about potential VIX dynamics as an asset class. We will also trade VIX Futures, VIX ETPs such as VXX and UVXY and also VIX Options on the platform so that you get a better sense of their similarities and differences and how those specific products can help you trade VIX more efficiently and profitably.

VIX calculation and settlement of VIX Futures and Options
VIX is one of the most important indices to follow for option traders. It represents the level of fear in the marketplace as reflected in the prices of SPX Options and measures the expected market volatility over the next 30 days. In this lesson we will go into the details of how the VIX is calculated so that we understand the intricacies of the VIX as compared to VIX products such as VIX Futures, Options and ETPs. We will also look at the cash settlement process for VIX Futures and Options and the similarities and differences between this special settlement value, which is available only on expiration day at market open, and regular VIX.
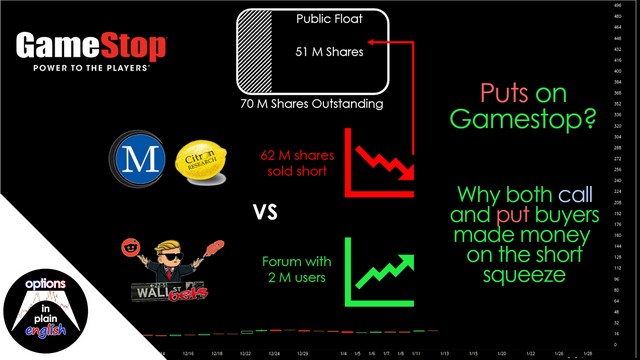
Puts on Gamestop? Why both call and put buyers made money on the short squeeze
It's obvious that call buyers were big winners after the Gamestop short squeeze. In this video you will learn why put buyers were also winners, despite being completely wrong about price direction (hint: with options, it's all about Implied Volatility)
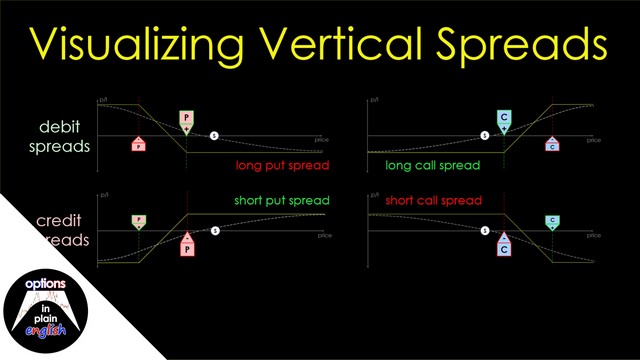
Visualizing Vertical Spreads: Call spreads and Put spreads in plain English
Vertical spreads are one of the most versatile and useful option strategies. They combine the exposure of stand-alone long or short calls or puts with the protection of pre-defined maximum losses and capital usage. In this lesson we take a look at Vertical spreads as we try to clarify the main reasons why option traders don't get the results they are hoping for when using either debit or credit spreads.